Should Scientist Be Permitted To Perform Experiments On Animals?
Abstract
The similarities betwixt sure animals and humans hateful that animal research tin be very useful in agreement how the human body works and in developing and testing new medicines. Many major medical breakthroughs have been fabricated with the help of animal experiments, including the invention of antibiotics, vaccines, and cancer treatments. However, some research can consequence in hurting and suffering for the animals, and although there are laws in place now to protect animals, it would be better if nosotros had alternative ways to move medical science forward. Scientists are working on new approaches that replace, reduce, and refine (improve) animate being experiments. This is known every bit the 3Rs of scientific research. Some of this work focuses on improving the housing for the animals, while other work involves using cells in a exam tube or computer models as beast substitutes. The three Rs are a stride in the right management for medical scientific discipline.
Introduction
Information technology would be risky to try a new medicine out on humans before checking that information technology is safe and that it works—people could become very ill or fifty-fifty die in the procedure. Considering there are many similarities between animals and humans, and they often become the aforementioned illnesses, animal experiments tin can assistance u.s.a. to understand different diseases and to pattern and examination new treatments for diseases. Mammals like mice, rats, and rabbits have the same set of organs including a brain, middle, and lungs that work in the same way they practice in humans. That ways the fauna experiments tin requite u.s. a reasonable thought of what might happen in a person. Even uncomplicated animals like fruit flies and worms can exist used to understand how our genes and immune systems piece of work.
Many major medical breakthroughs take been made due to animal experiments. For example, in the 1920s, a surgeon discovered he could salve the symptoms of diabetes in dogs past injecting them with insulin. Before that, people with diabetes got very sick and did not live for long, but at present with the assist of insulin, diabetics are able to command the level of sugar in their claret and live normal lives. Animals have been used to develop vaccines to prevent diseases that previously killed billions of people, including polio and meningitis. Creature experiments too allowed us to develop crucial medical practices we at present have for granted, like anesthetics to put people to slumber during surgery, cancer treatments, and antibiotics. While a person born 100 years ago would be expected to live for 30 years, people born these days live around seventy years. Discoveries resulting from animal experiments have a lot to do with that increment in lifespan.
However, fauna research comes at a toll to the animals, and it is sometimes unavoidable that they will experience pain and suffering. For instance, the animals might exist given injections, surgery, or an affliction like cancer, in order to test new medicines. The procedures carried out on animals are classified as "balmy," "moderate," or "severe" depending on the level of suffering. Nigh two-thirds of brute experiments are carried out on mice, and 8% of these are considered severe.
The Law
In the by, there were no laws in place to control how animal experiments were carried out and some of those experiments acquired unacceptable suffering to the animals. Thankfully, in 1876, the UK Parliament passed the "Cruelty to Animals Act," which meant researchers had to follow a list of rules and would be regularly inspected and would face consequences for cruelty. This human activity as well meant that fauna experiments could only exist performed if they were absolutely necessary and would help to relieve human lives, not only because the scientists were curious.
In the 1980s, the police was updated, and at that place are now very precise instructions on how to care for the animals besides equally which experiments can and cannot exist done. Scientists have studied animals to work out the best living conditions for them, and this information is used when writing the rules that scientists must follow. All research plans go judged beforehand to make certain the pros outweigh the cons, and these plans must be approved by specialist vets. At that place are besides laws banning the utilize of dandy apes similar chimpanzees and gorillas in U.k. research; nigh all experiments are washed on mice, rats, fish, and birds. Testing of cosmetics (like shower gel and shampoo) and household products (like detergents) is at present illegal in many countries, including Europe and India.
In the The states, the Animal Welfare Human activity was introduced in 1966 and is a federal police force that protects mammals used in scientific inquiry.
The 3Rs
Although important discoveries have been fabricated and there is much improvement in how laboratory animals are treated, we would all prefer it if we did not have to apply animals in experiments at all. So, are scientists doing anything to detect alternatives? The answer is a resounding yeah! 50 years ago, Bill Russell and Rex Burch wrote a book that introduced the "3Rs" for scientific enquiry [1]. Rather than reading, writing, and arithmetic (equally you may have come across in school), Bill and Rex were referring to replacement, reduction, and refinement. Replacement is almost finding different options for experiments, other than animals, and reduction is about developing methods so that fewer animals are needed in each experiment. Refinement is concerned with improving current animate being research and so that the animals suffer as little equally possible.
The 3Rs are now used in deciding the laws effectually animal research, and these days no experiment tin can be performed if there is an alternative available that does not use animals. Each experiment has to apply the minimum possible number of animals, and the method has to event in the to the lowest degree pain and suffering for the beast. Research using animals in the U.s.a. is regulated by the Us Department of Agriculture. In the UK, there is a specialized organization called the National Middle for the 3Rs (NC3Rs), 1 which supports piece of work to develop new enquiry methods that replace, reduce, or refine the use of animals.
Replacement
The ultimate replacement for brute experiments would be to use humans or human blood or tissue samples, equally the results of man experiments would exist the most accurate and relevant to humans. This is not possible in many cases because of the risks involved, but a method chosen "micro-dosing" is existence developed, in which people are given tiny amounts of new medicines to look at how their immune systems respond. Animals like mice and rats can also sometimes exist replaced with other living things that are not thought to be able to experience suffering, like fruit flies. Worms accept recently been used to detect new antibiotics.
I option for replacing animals is to use in vitro models. "In vitro" literally ways "in the glass" and refers to studies performed in a test tube in the laboratory, rather than within a person or animal (which would be chosen in vivo). Using in vitro models, complicated systems in the trunk are simplified and then that scientists tin concentrate on the one office they are interested in and they tin can run lots of experiments in a short amount of time. In vitro work has resulted in many important discoveries, including the identification of antibodies, which are a key part of the immune system that recognizes microbes and helps to destroy them.
In our laboratory at the Academy of Oxford, we are developing an in vitro model to exam new vaccines. Normally, to test if a new vaccine works against a certain disease, for example, tuberculosis , scientists would immunize animals with the vaccine and so infect them with tuberculosis to encounter if they are protected. With our in vitro method, nosotros infect cells (often human cells) in a test tube and then that no animals need to get sick. We tin can compare whether cells from vaccinated animals or people are better at killing the tuberculosis bacteria than are cells from non-vaccinated animals or people [2]. Other scientists use similar systems to test new medicines and check if they are safe and if they work.
One of the bug with in vitro models is that they may exist as well unproblematic and therefore might not predict what would happen inside an bodily body. For example, a medicine that kills a virus in a test tube might not kill information technology inside an animal, because the virus can hibernate away in sure parts of the animal's trunk. Or the medicine might appear prophylactic in vitro, but crusade side effects in parts of the body that were not represented in the examination tube. Scientists are now trying to overcome these problems past building 3D in vitro models. These are more than complicated and involve lots of different types of cells that come together to form something similar to a whole organ, like a liver or a heart.
Some other mode of replacing beast experiments is by using computers or mathematical models. These utilize calculations based on previous research to predict which medicines might be effective or which side effects might occur if the medicines were given to humans. Contempo advances in technology mean that computers can simulate real biological processes in a virtual reality. Such methods take been used to develop vaccines based on information almost bacterial genes and take also been used in cancer inquiry to model tumors. One group at the Academy of Oxford built a calculator model to examination how drugs might touch on the heart [3]. The unlike ways of replacing animal experiments are summarized in Figure 1.
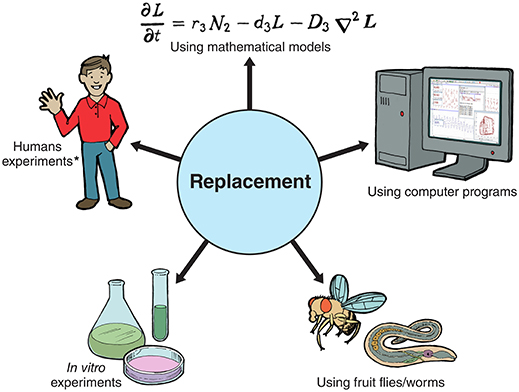
- Figure 1
- Summary of the different ways of replacing brute experiments with other types of experiments. * The Nuremberg lawmaking - a prepare of enquiry ideals principles for human experimentation - requires that human experiments are based on the results of animal experiments, in club to protect humans from damage. Even so, there are some situations in which homo volunteers may be used in place of animals - for example we tin sometimes study the immune response in people who have been naturally infected with a illness rather than infecting animals experimentally.
Reduction
To reduce the number of animals used in enquiry, experiments have to be carefully designed and analyzed. If too few animals are used in an experiment, whatever difference between groups (for example, if an experiment was testing groups of mice receiving dissimilar medicines to see which was safest) might be unclear and the experiment would take to be repeated. Repeating the experiment would use fifty-fifty more animals in the long run.
Scientists are also trying to maximize the amount of information they tin get from each animal. For example, if they are looking at the progression of a tumor, they might need to sacrifice different animals each calendar week to look inside at the size of the tumors. By scanning the tumors instead, the aforementioned animals can be assessed each week and fewer are used overall.
Sharing results between different groups of researchers and organizations, by writing manufactures and giving presentations, makes it less likely that the same experiments get repeated unnecessarily by different people. Publishers of some scientific journals are helping with this past agreeing to share results that might not otherwise be available. The different means of reducing the number of animals used in experiments are summarized in Figure 2.
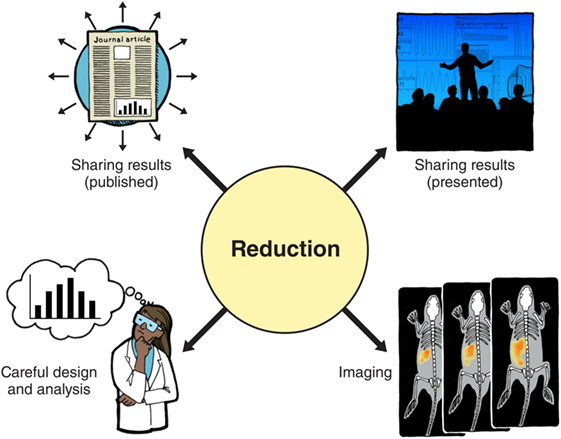
- Figure 2
- Summary of the different ways of reducing the number of animals used in experiments.
Refinement
Refinement is about minimizing pain and suffering and improving the health and happiness of the animals. Refinement includes making sure the animals have comfortable housing conditions that support their natural needs like socializing, hiding, gnawing, and nest building. In that location are at present rules in place almost the size of cages needed and the kinds of toys, hiding places, and bedding fabric that should be provided. Scientists at the Academy of Liverpool have been studying the all-time mode to choice upward mice to minimize their stress [4]. Others at the University of British Columbia establish that rats adopt to have burrowing materials and the opportunity to climb [five].
Ane important refinement in creature experiments is using imaging technologies instead of invasive techniques like surgery or taking blood. Rather than catastrophe an animal's life to observe how a disease has spread inside the trunk, pictures can be taken with minimum disturbance while the animal is alive. Imaging tin exist done with X-rays or scans, or by making parts of the animal's trunk "glow in the dark," using chemicals that occur naturally in algae and jellyfish. Many scientists at present monitor malignant tumor growth and infections with viruses or leaner in this fashion. They can even use these methods to look at where medicines travel in the body. Making experiments shorter and using better hurting relief are also methods of refinement. The different ways of refining animal experiments are summarized in Effigy 3.
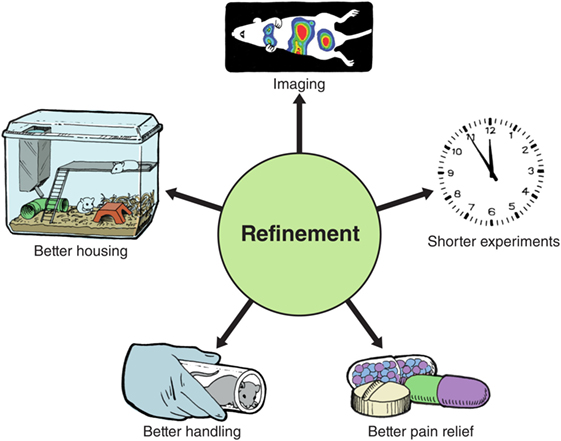
- Figure iii
- Summary of the different ways of refining (improving) animal experiments.
Conclusion
Many important medical discoveries take resulted from animal research and endless human lives accept been improved or saved by experiments using animals. Animal testing has come up a long fashion since the unregulated experiments of the terminal century and there are now strict laws in place to protect animals and preclude suffering. However, anybody would prefer it if nosotros could stop using animals in medical research altogether.
Scientists around the globe have been working hard to detect new methods to supersede the utilize of animals, reduce the numbers of animals used, or improve the experiments to minimize fauna suffering. This is in line with the 3Rs principles of scientific research. Most research is now carried out using alternative methods and the number of laboratory animals used in the Uk has been reduced by one-half in the concluding 30 years, but animals all the same need to exist used in many situations. Bodies are so complicated that nosotros cannot always know how they will react to a disease or medicine just by looking at cells in a test tube, or at a computer program or fruit flies. Nevertheless, as technology advances in the future and scientists go along to piece of work on the 3Rs, there is hope that one day laboratory animals will only be found in history books.
Glossary
Genes: ↑ The biological "instructions" passed downwards from our parents, which make up one's mind our characteristics.
Allowed Organisation: ↑ Our natural protection against disease-causing organisms similar leaner and viruses.
Diabetes: ↑ A lifelong status that causes the level of sugar in a person's claret to become likewise high. This is because the pancreas does non produce enough of the hormone insulin, or the cells in the body are non responding properly to the insulin that is produced.
Vaccine: ↑ Pocket-size amounts of weak or dead bacteria or viruses that help prepare the allowed system to fight the affliction faster and more effectively, to prevent sickness.
Tuberculosis: ↑ A affliction that mainly affects the lungs and is acquired by bacteria that can be spread past the coughs and sneezes of an infected person.
Imaging Technologies: ↑ Creating pictures of the inside of a body for analysis. These include techniques such equally X-rays and ultrasound.
Conflict of Interest Argument
The author declares that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or fiscal relationships that could be construed as a potential disharmonize of involvement.
Acknowledgements
I would like to thank Daniel McShane for his critical reading of this article and the NC3Rs for their back up of my research.
References
[1] ↑ Russell, W., and Burch R. 1959. The Principles of Humane Experimental Technique. Wheathampstead, Britain: Universities Federation for Brute Welfare.
[ii] ↑ Brennan, Chiliad. J., Tanner, R., Morris, Due south., Scriba, T. J., Achkar, J. Thousand., Zelmer, A., et al. 2017. The cross-species mycobacterial growth inhibition assay (MGIA) project, 2010-2014. Clin. Vaccine Immunol. 24(9):e00142–17. doi:x.1128/CVI.00142-17
[3] ↑ Britton, O. J., Bueno-Orovio, A., Van Ammel, Thou., Lu, H. R., Towart, R., Gallacher, D. J., et al. 2013. Experimentally calibrated population of models predicts and explains�intersubject variability in cardiac cellular electrophysiology. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. United statesA. 110(23):E2098–105. doi:10.1073/pnas.1304382110
[iv] ↑ Gouveia, K., and Hurst, J. L. 2013. Reducing mouse anxiety during treatment: effect of experience with handling tunnels. PLoS ONE viii(6):e66401. doi:ten.1371/journal.pone.0066401
[five] ↑ Makowska, I. J., and Weary, D. Yard. 2016. The importance of burrowing, climbing and standing upright for laboratory rats. R. Soc. Open Sci. 3(6):160136. doi:ten.1098/rsos.160136
Footnote
[one] ↑ https://nc3rs.org.uk/ (Accessed: May 22, 2018).
Source: https://kids.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/frym.2018.00044
Posted by: mccluskeyvarty2001.blogspot.com

0 Response to "Should Scientist Be Permitted To Perform Experiments On Animals?"
Post a Comment